Add README.md
This commit is contained in:
parent
813268fcf8
commit
1318347fd8
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
|||
# Home Assistant Polymer
|
||||
|
||||
This is the repository for the official Home Assistant frontend. The frontend is built on top of the following technologies:
|
||||
|
||||
* [Polymer](https://www.polymer-project.org/1.0/)
|
||||
* [NuclearJS](http://optimizely.github.io/nuclear-js/)
|
||||
* [ES2015 via Babel](http://babeljs.io/)
|
||||
* [WebPack](http://webpack.github.io/)
|
||||
* [Bower](https://bower.io) for Polymer package management
|
||||
* [NPM](https://npmjs.com) for JavaScript package management
|
||||
|
||||
[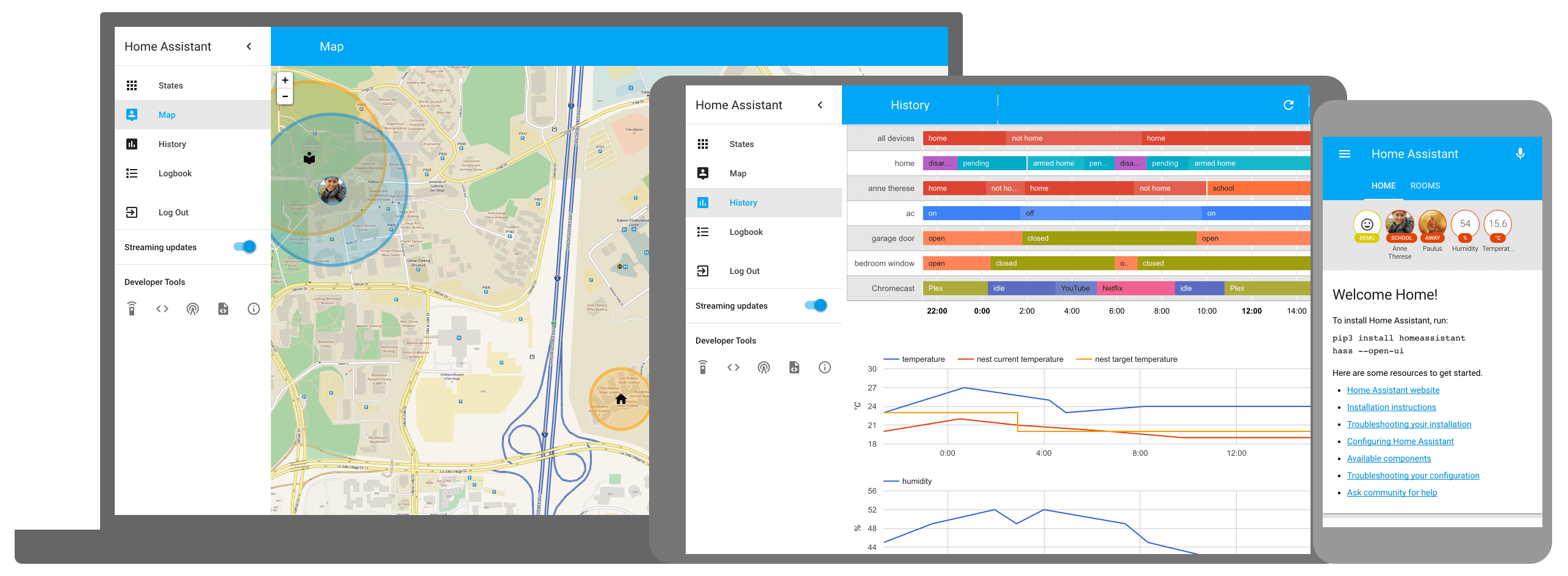](https://home-assistant.io/demo/)
|
||||
|
||||
## An unusual approach to Polymer
|
||||
|
||||
As you might have noticed, we are using two different package managers. This might seem crazy but we have good reasons. Let us explain…
|
||||
|
||||
One of the big advantages of webcomponents is that you can ship all your HTML resources in a single file: HTML-template, CSS and JavaScript. From your HTML template and JavaScript you are then able to embed extra webcomponents and use it to build a whole UI.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Before the release of Polymer 0.8, you would define all parts of your webcomponent inside a `<polymer-element>`. With the introduction of Polymer 0.8 the structure of a webcomponent has been split up into a `<dom-module>` for the CSS and HTML template and a `<script>` calling the `Polymer` object to register your element.
|
||||
|
||||
The JavaScript ecosystem is evolving at a rapid pace and most projects have been embracing the next generation of JavaScript, EcmaScript 2015. Home Assistant did too and our [JavaScript backend](https://github.com/balloob/home-assistant-js) has been written in ES2015 for a while now. To get our webcomponents to interface with the backend, we would expose objects on the window object. This lead to pollution of the global namespace and messy component code.
|
||||
|
||||
For Polymer, it does not matter if the file that registered the webcomponent is the same file that embeds the webcomponents CSS and HTML template. We used this to our advantage and created a JavaScript module for each webcomponent. Just like the HTML-based webcomponents, it will import the webcomponents it depends on. We now have one tree of HTML webcomponents that include all required HTML-webcomponents and a tree of JavaScript webcomponents that include all required JavaScript webcomponents. The downside of this approach is that we express each relationship between webcomponents twice, but for a good reason: we are now able to use all the popular JavaScript tools with Polymer!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Building the app
|
||||
|
||||
The Polymer team has developed [Vulcanize](https://github.com/polymer/vulcanize) to help you prepare your webcomponents app. It takes an HTML file and recursively embeds referenced HTML, JavaScript and CSS files. There are similar approaches available for JavaScript that will resolve all referenced JavaScript modules and output a single file. For Home Assistant we have chosen to use WebPack. Babel is a plugin for WebPack to allow it to translate EcmaScript 2015 syntax into JS5 syntax.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead of having each webcomponent reference its own JavaScript file, we now have the root webcomponent of the web app refer to the compiled JavaScript after all HTML templates have loaded. The final vulcanized output of our app will contain all the CSS and HTML templates first, and then all the JavaScript.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## The tale of two package managers
|
||||
|
||||
The CSS and HTML template part of our webcomponents can depend on our own or third party webcomponents. Currently bower is the only way webcomponents are being distributed. This cannot be done via NPM because NPM only distributes JavaScript files and no CSS or HTML templates.
|
||||
|
||||
For our JavaScript we want to have fine grain control of which parts of our third party components get included, which is possible using NPM. For example, instead of importing the whole lodash library, we only [import the functions that we will use](https://github.com/balloob/home-assistant-polymer/blob/8e143c2e4461771a51cdead553b7fa9e5bbdf772/src/components/state-history-chart-line.js#L1-L4).
|
||||
|
||||
## License
|
||||
Home Assistant is open-source and MIT licensed. Feel free to browse the repository, learn and reuse parts in your own projects.
|
||||
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 25 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 352 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 15 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 17 KiB |
|
|
@ -3,8 +3,6 @@ var fs = require('fs');
|
|||
|
||||
var html = fs.readFileSync('build/frontend.vulcan.html').toString();
|
||||
|
||||
// removeComments: true,
|
||||
// collapseWhitespace: true,
|
||||
var minifiedHtml = minify.minify(html, {
|
||||
customAttrAssign: [/\$=/],
|
||||
"removeComments": true,
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue